Author Archive
Vapor-worm Day..
by Brian on Feb.01, 2006, under Windows Info
KamaSutra/Blackworm Disinfection Utility*
F-Secure Corporation provides the special disinfection utility to clean Nyxem.e infection from a computer. This disinfection utility is called F-Force and it can be downloaded from F-Secure’s web and ftp sites:
ftp://ftp.f-secure.com/anti-virus/tools/f-force.zip
http://www.f-secure.com/tools/f-force.zip
The utility is distributed only in a ZIP archive that contains the following files:
- f-force.exe – the main executable file
- eult.rtf – End User License Terms document
- readme.rtf – Readme file in RTF format
- readme.txt – Readme file in ASCII format
To unpack the archive please use the WinZip or similar archiver.
IMPORTANT! Please make sure that you read the End User License Terms document (Eult.rtf) and the Readme file (either Readme.txt or Readme.rtf) before using the F-Force utility!
The F-Force utility needs the archive with the latest updates in order to function properly. The archive’s name is LATEST.ZIP and it should be downloaded and put into the same folder where the F-Force utility is located. This archive with the latest updates can be downloaded from these locations:
http://download.f-secure.com/latest/latest.zip
ftp://ftp.f-secure.com/anti-virus/updates/latest/latest.zip
Please note that the F-Force utility can disinfect only certain malicious programs. Besides the utility does not scan inside archives. So after cleaning a computer with the F-Force utility it is recommended to scan all hard drives with F-Secure Anti-Virus and the latest updates to make sure that no infected files remain there.
A trial version of F-Secure Anti-Virus and the latest updates can be downloaded from F-Secure’s website:
http://www.f-secure.com/download-purchase/list.shtml
http://www.f-secure.com/download-purchase/updates.shtml
* taken from f-secure.com
Seamonkey 1.0 Released!
by Brian on Jan.31, 2006, under Windows Info
For those of you that really missed Netscape Communicator, this will be a welcome addition to your arsenal. Seamonkey 1.0 has it all, a web browser, advanced e-mail and newsgroup client, IRC chat client, and HTML editing made simple — all your Internet needs in one application. Basically, all the great tools Communicator had, with some new bells and whistles from the fine folks at Mozilla.org. You can get your copy here.
Installing an OpenBSD VirtualPC on a Mac
by Brian on Jan.22, 2006, under Mac OSX, OpenBSD
The following directions are for OpenBSD and Virtual PC on the Macintosh, and assume familiarity with the installation and use of both. Note that if you have OpenBSD CDs, you may boot off the i386 CD to perform the installation. Please refer to either the OpenBSD/i386 installation documentation or the Virtual PC documentation in case of questions, as documenting the installation of either is beyond the scope of this document.
- Grab(buy) the latest OpenBSD release. (there’s a link on the Links page)
- Create a Virtual PC hard disk image file of the size you want your OpenBSD hard disk to be, at least a gigabyte if you want to unpack the source tree and have a usable system. However, you can get away with a hard disk as small as 300MB or so for a complete installation.
- Change the VirtualPC partition to use a fixed file size on your local disk. You *CANNOT* use a dynamically re-sizable partition. The only drawback to this is that a 10gb partition takes up 10gb, even if most of it is empty space. OpenBSD does not like dynamically resizing partitions, and installing OpenBSD on one of these will hang while extracting base3x.tgz. (or it will hang on misc3x.tgz if it makes it through base3x.tgz)
- Capture your OpenBSD CD or the cd38.iso image to the VirtualPC’s cdrom drive.
- Start up the VirtualPC, and boot to the captured CD image.
- Perform OpenBSD install as usual.
- Shut down the virtual machine with halt… Welcome to OpenBSD: The proactively secure Unix-like operating system.
Using Multiple Pre-Shared Keys with OpenBSD ISAKMPD
by Brian on Jan.02, 2006, under OpenBSD
Having an Open Source IPSec VPN into the office is nifty. It usually also means others will want to appreciate it’s niftiness… (and use your bandwidth to check their Exchange calendars). So, do you want 30 or so other users out there with their perpetually un-locked, spyware and virus-vulnerable XtraPenetrable laptops, holding the only pre-shared key to your VPN? Of course not. (you really don’t). So, implement one pre-shared key per user, or one key per group, depending on your policy of access revocation.
We really like OpenBSD around here, and may sound like men with a hammer thinking everything is a nail, but it really does do *everything* well as far as we use it. So here’s the setup.
First, you must create the config files for ISAKMPD.
$ sudo touch /etc/isakmpd/isakmpd.conf
$ sudo touch /etc/isakmpd/isakmpd.policy
Then, turn on the AH and ESP protocols by editing the /etc/sysctl.conf.
net.inet.esp.enable=1 # 0=Disable the ESP IPsec protocol
net.inet.ah.enable=1 # 0=Disable the AH IPsec protocol
Or, just do it from the shell-
$ sudo su
# sysctl -w net.inet.esp.enable=1
# sysctl -w net.inet.ah.enable=1
Now, we’ll set up a basic road-warrior configuration in /etc/isakmpd/isakmpd.conf .
Here’s an example.
Next, we’ll set up the multiple pre-shared keys in the policy file.
Here’s another example.
After we edit these files, you’ll need to change the permissions on them.
$ sudo su
# chmod 0500 /etc/isakmpd/isakmpd.conf /etc/isakmpd/isakmpd.policy
Now allow the VPN traffic through your packet filter-
Here’s another example.
Apply the new packet filter configuration:
# pfctl -f /etc/pf.conf -F all -d -e
Fire up ISAKMPD in debug mode so you can see any incoming connections
$ sudo su
# isakmpd -d -DA=75
Once your road-warrior connects successfully, kill the debug mode ISAKMPD and start it in normal daemon mode.
$ sudo su
# pkill -9 isakmpd && isakmpd
Now, connect a road-warrior machine to the outside of your firewall, and check for your security associations.
$ sudo su
# ipsecadm show
If you have a valid VPN connection, you should see something like this:
sadb_dump: satype esp vers 2 len 40 seq 0 pid 0
sa: spi 0x80655c1b auth hmac-sha1 enc 3des-cbc
state larval replay 0 flags 4
lifetime_cur: alloc 0 bytes 0 add 1136234418 first 0
lifetime_soft: alloc 0 bytes 0 add 0 first 0
lifetime_hard: alloc 0 bytes 0 add 28800 first 0
address_src: 192.168.245.2
address_dst: 192.168.209.2
identity_src: type prefix id 0: 192.168.245.2/32
identity_dst: type prefix id 0: 192.168.209.2/32
key_auth: bits 160: 9dfde94cd9708d6a995a4d238
key_encrypt: bits 192: 3bc2f3f7f0fbce8a12ae73966c5
sadb_dump: satype esp vers 2 len 40 seq 0 pid 0
sa: spi 0x895dcf4b auth hmac-sha1 enc 3des-cbc
state larval replay 0 flags 4
lifetime_cur: alloc 0 bytes 0 add 1136261627 first 0
lifetime_soft: alloc 0 bytes 0 add 25920 first 0
lifetime_hard: alloc 0 bytes 0 add 28800 first 0
addres_src: 192.168.245.2
addres_dst: 192.168.209.2
identity_src: type prefix id 0: 192.168.245.2/32
identity_dst: type prefix id 0: 192.168.209.2/32
key_auth: bits 160: 9d8c52703983b1497b655a9
key_encrypt: bits 192: 39875c4b8fd77ec740f37da27d
You can also check the VPN connections with netstat-
$ sudo su
# netstat -rn
Should output something like this-
Encap:
Source Port Destination Port Proto SA(Address/Proto/Type/Direction)
192.168.0/24 0 192.168.10/24 0 0 192.168.245.2/50/use/in
192.168.10/24 0 192.168.0/24 0 0 192.168.209.2/50/require/out
I realise this is short, (I wasn’t paid to write this book) ;) so please feel free to post any questions or comments.
KDE 4 to support Apple's Dashboard Widgets!
by Brian on Jan.02, 2006, under Mac OSX
As seen here, the KDE project is working on the integration of Apple’s Dashboard widgets. One more reason to run *nix on PPC hardware.
Samsung SC-D353 SMP4 AVI codecs conversion
by Brian on Dec.29, 2005, under General Info
I got a new toy for Christmas. It’s a Samsung SC-D353 Digital Video camera. It has a 1gb 40x memory stick, takes Mini-DV tapes, and has S-video, DV, and USB outs. So, I shot a few seconds of video, plugged the USB cable into the trusty powerbook, and… nothing.
Not even an error sound.
Odd… The powerbook can do *anything*. (can’t it?) hmm….
Ok, the first thing that I noticed was the camera was set to use USB 2. I changed the USB setting to use 1.1 with the camera’s setup menu, and now I can mount the memory stick as USB storage. COOL!!!! (told ya they can do anything…) There’s my .avi files, ready to view. Copied them down to the desktop, and double clicked on one. OK, now we have sound, but no video. Just white screen.
After some research, I found that Samsung wrote their own AVI codecs. (SMP4) You can download it here:
http://www.samsung.com/download/
Ok, but if we want to send this video to someone, (grandma), she’s not going to be able to grep google for the proper codecs, now will she?
So, we need to convert this video to something other than Samsung’s best guess at encoding. How about WMV? Most newbie users can see those without too much trouble, right?
Back to grepping google, I found a freeware video conversion utility for windows called VideoPak.
You can dowload a copy here:
http://www.tucows.com/preview/340342
This utility will allow the conversion of Samsung’s AVI format to everyday, normal WMV.
You can also specify the intended target for distribution, (broadband web video, email, streaming, etc)
I ran VideoPak on a 6mb AVI, and compressed it to 768k video for broadband, and it came out as a 1.9mb WMV.
Snort Reports with SnortALog
by Brian on Dec.27, 2005, under Networking, OpenBSD
SnortALog v2.4.0 is a really nice Snort logfile reader/parser/perl script written by Jeremy Chartier. Thank you Jeremy! It’s an *incredible* piece of work! Get a copy from his website. I installed mine on OpenBSD-3.8-STABLE, but I also needed the p5-GD-Graph package from the ports tree.
$ cd /usr/ports/graphics/p5-GD-Graph
$ sudo make install
Then, I made the script to run SnortALog, and set it to run from root’s crontab.
Here’s a screenshot of the HTML output.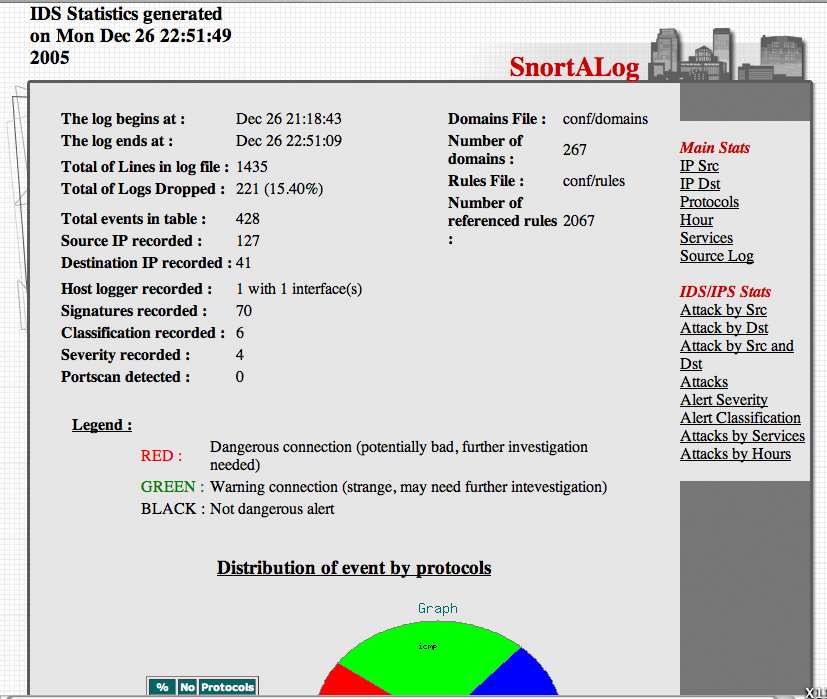
Graphing packet traffic with pf & pfstat
by Brian on Dec.21, 2005, under Networking, OpenBSD
Getting a good visual representation of your network traffic has never been easier. We use OpenBSD for most of our firewalling applications, and for VoIP/VPN solutions. As a result, we (as well as our customers) need to closely track the bandwidth utilization of some of the endpoints for quality of (VoIP) service reasons. RRDTool and MRTG are both very excellent tools, but what to do when snmp is not an option? Pfstat, available in the OpenBSD ports tree, solves this problem, and is *considerably* easier to install and configure.
First, install pfstat.
$ cd /usr/ports/net/pfstat
$ sudo make install
Now, set it up.
you need to create a few files first.
$ sudo touch /var/log/pfstat
$ sudo touch /etc/pfstat.conf
Now, set up the /etc/pfstat.conf file you just created.
$ sudo vi /etc/pfstat.conf
Here’s an example pfstat.conf I found on benzedrine.cx, (the homepage of the author of pf & pfstat) and modified just slightly.
Thank you, Mr. Hartmeier. Your work is amazing.
Speaking of Pf, we need to edit the packet filter configuration, to set the log interfaces.
$ sudo vi /etc/pf.conf
Now, find your interface names. (Mine are $ext_if=rl0 and $int_if=fxp0)
So, I added the following lines to the /etc/pf.conf
set loginterface rl0(It has been pointed out that this is incorrect.
set loginterface fxp0
The last interface listed is the one that will get used. Thanks, Jon.)
Fetch the new packet filter configuration:
$ sudo pfctl -f /etc/pf.conf
Now, edit root’s crontab to run pfstat and update your graphs.
$ sudo su
# crontab -e -u root
and add the following two lines to it:
* * * * * /usr/local/bin/pfstat -q >>/var/log/pfstat
*/5 * * * * /usr/local/bin/pfstat -c /etc/pfstat.conf -d /var/log/pfstat >/dev/null
Hold “Shift” and hit “ZZ” to save and exit root’s crontab.
To force the creation of the graph images, run this:
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/pfstat -q >>/var/log/pfstat
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/pfstat -c /etc/pfstat.conf -d /var/log/pfstat >/dev/null
Now, you just need an HTML document to display your nifty new graphs.
Here’s the one I use.
Save it to /var/www/htdocs/traffic_stats.html, and start up apache:
$ sudo apachectl start
and check out your traffic:
http://your.web.server/traffic_stats.html
.
virii and crackers and worms, oh, my!
by Brian on Dec.20, 2005, under Amusement
Crackers (*not hackers, people… Crackers.) have penetrated(?) the *un-encrypted* customer information database of a large security software company.
US Government agency credit card and personnel info may be at risk.
Read the Washington Post article here.
Registrations turned on
by Brian on Dec.13, 2005, under General Info
You may now register for this site here.
Or, scroll down to the bottom and click on “Register”
See that? nice and simple.
addresses will be held in strictest confidence.
(I probably won’t even look at them. ;)

